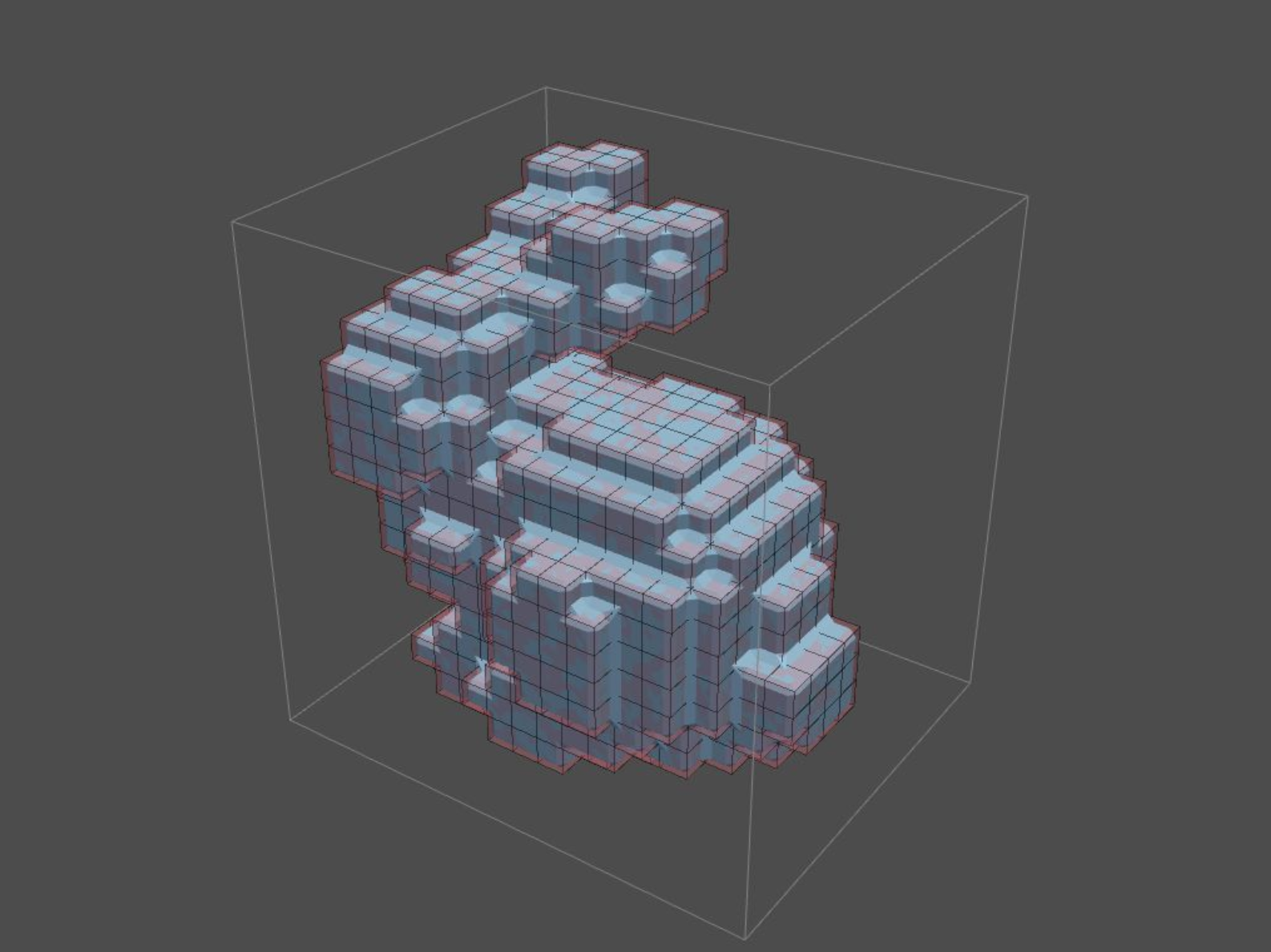
Boolean Marching Cube¶
In this notebook we will go through the following process: 1. Surface Mesh Sampling 2. Voxelization 3. Boolean Marching Cube
0. Initialization¶
import all the necessary libraries and specify all inputs
import os # for path manipulation
import topogenesis as tg# core
import pyvista as pv # for plotting and visualizations
vs = 0.01 # voxel size
unit = [vs,vs,vs] # unit size
tol = 1e-09 # intersection tolerance
mesh_path = os.path.relpath('../../data/bunny_lowpoly.obj')
original_mesh = tg.geometry.load_mesh(mesh_path)
1. Mesh Sampling¶
Now that we have everything in place we will run the sampling algorithm to construct a point cloud based on our original_mesh
sample_cloud = tg.geometry.mesh_sampling(original_mesh, unit, tol=tol)
2. Voxelization¶
Voxelating the point cloud to construct the lattice
lattice = sample_cloud.voxelate(unit, closed=True)
3. Boolea Marching Cube¶
Costructing the Cube Lattice using the Boolea Marching Cube Algorithm
cube_lattice = lattice.boolean_marching_cubes()
4. Plotting¶
# initiating the plotter
p = pv.Plotter(notebook=True)
# visualize tiles
p = tg.marching_cube_vis(p, cube_lattice, "chamfer")
# fast visualization of the lattice
p = lattice.fast_vis(p)
# adding the base mesh: light blue
# mesh = pv.read(geo_path)
# p.add_mesh(mesh, show_edges=True, color='#abd8ff', opacity=0.4, label="Base Mesh")
# plotting
p.show(use_ipyvtk=True)